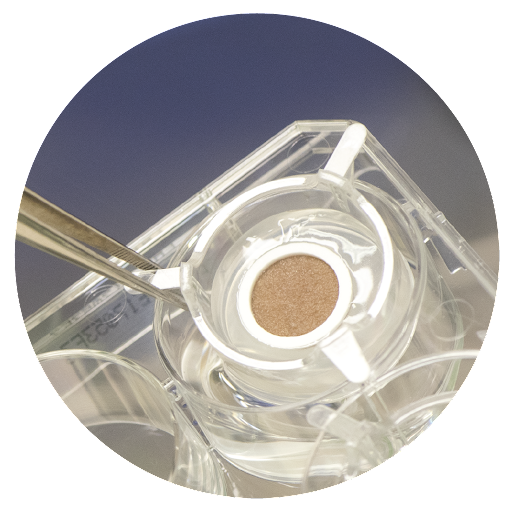
NativeSkin® human skin models
live first-in-human data generation
The NativeSkin® live human skin model
A cruelty-free highly predictive model for relevant study results

NativeSkin® human skin models provide the closest alternative to directly testing on a real person’s skin. NativeSkin® models are round human skin biopsies contained in a patented matrix that keeps them alive and functional. The model is designed to offer an innovative study platform for research and analysis to study the response of real, live human skin to compounds, drugs, cosmetics and medical devices after topical or systemic administration. A quick overview of the model’s features and benefits:
Immunocompetent
NativeSkin® models hold the features and functionalities of in vivo human skin, with all cells and appendages, to generate predictive human data.
Human
The models only contain real, donated human skin and are animal component free (ACF) / xeno-free (XF) for research and cosmetic testing.
Skin
NativeSkin® models are standardized to allow for reproducible research and testing on real, live human epidermis and dermis.
On Demand
NativeSkin access® skin models can be ordered online but our experts can also help you design the perfect NativeSkin® study to fit your needs.
Live response from real human skin
A full week of testing opportunities
The NativeSkin® model is a live, patented ex vivo human skin model that contains round human skin biopsies from donated surgical discards. The skin is kept alive thanks to Genoskin’s patented technology, which allows keeping real human skin in a living state for 7 days. This approach helps us provide a highly relevant and reliable solution to pharmaceutical, biotech, cosmetic and chemical companies to test their compounds on real human skin for an entire week, without harming either humans or animals.
NativeSkin® keeps things real
Real human skin for real human data




As opposed to animal skin, bioprinted skin, human skin equivalents or reconstructed skin, NativeSkin® keeps things real. It truly is the real deal: NativeSkin® is human skin and it’s alive. It offers a valid, more reliable alternative to animal testing for predictive first-in-human data prior to clinical trials. Naturally, both the model and its culture medium are animal component free (ACF) / xeno-free (XF).
Ethical compliance & sourcing procedures
Official authorizations from French & US institutions
Approved by the Ethical Committees
Informed Consent from every donor
Secure agreements with contributing hospitals and clinics in France and in the US
Real human epidermis & dermis with all cells, appendages and characteristics
Maintained skin barrier function, tissue integrity, morphology and physiology
Live human skin response to your compound, drug or cosmetic
Animal component free (ACF) / xeno-free (XF) model and culture medium
Safety tested for Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, HIV 1 & 2
Donor information on age, gender, skin type, allergies, skin conditions and specific dermatological treatments
Informed consent
Informed consent from all donors, in compliance with all applicable regulations
Compliant procedures
Skin sourcing approved by all mandatory institutions in France and the US
Ethical & secure sourcing
Secure agreements with hospitals and clinics
Standardized production
Compliant & standardized production for reproducible results
Scientific validation in terms of skin structure
Human skin structure is maintained for +7 days
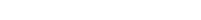
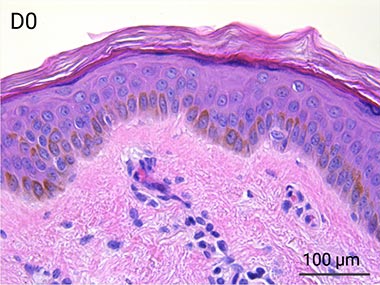
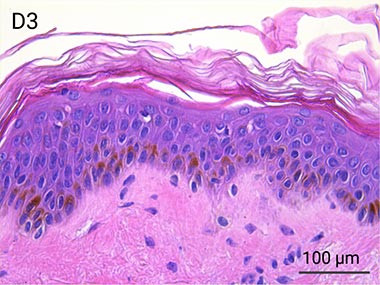
Since it is real human skin, NativeSkin® has the same structure and composition as in vivo human skin. It presents a mature stratum corneum and normal skin barrier function and their integrity can be preserved for 7 days. After 7 days of culture, experimental data may show higher variability but NativeSkin® remains viable. Hematoxilin & Eosin staining shows mature stratum corneum, a dermal-epidermal junction that comprises the key features of the dermal-epidermal junction of real human skin, with a preserved basal layer and rete ridges. The images also illustrate that dermis integrity is preserved for 7 days.



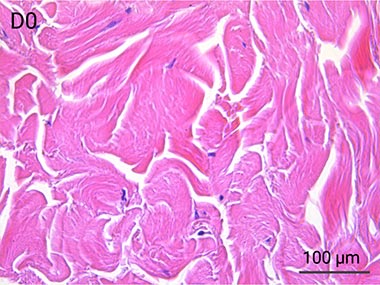

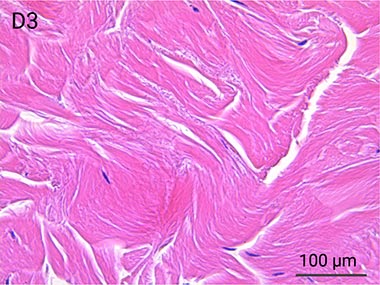

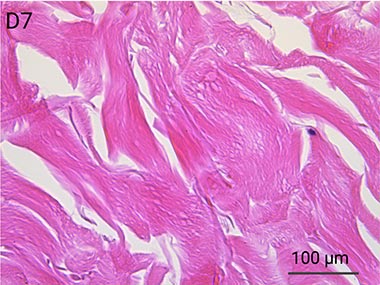

Scientific validation of live human skin response
NativeSkin® models show real human skin response




Even though cell interaction may vary from one person to another and one skin type to the next, live cell interaction remains crucial when it comes to estimating the response of human skin to certain compounds. Thanks to Genoskin’s patented matrix, immune cells remain present and viable in NativeSkin®, allowing for real human skin response.
Exposure of NativeSkin® to pollution
To better characterize the consequences of exposure to pollution on human skin homeostasis, we incubated NativeSkin® models in a pollution chamber every day for four days. The pollution chamber was designed to mimic chronic low-level environmental exposure of five Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): hexane, toluene, acetaldehyde, formaldehyde and acetone. Results are shown below. You’ll find all the study details here.
Cell viability
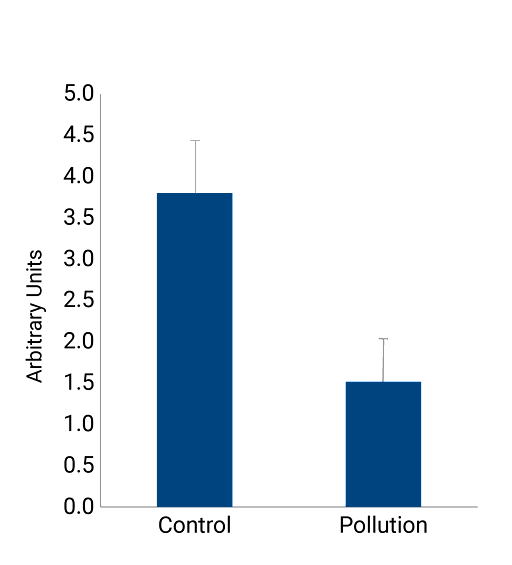
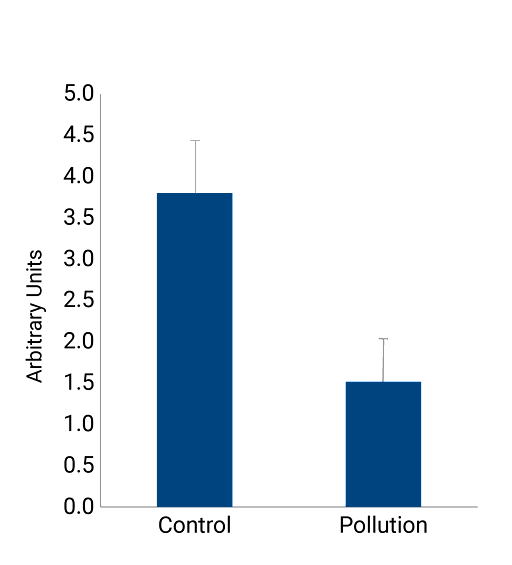
Pollution induces an important decrease in cell viability in NativeSkin®. This MTT assay shows a decrease of about 60% in cell viability.
Cell proliferation
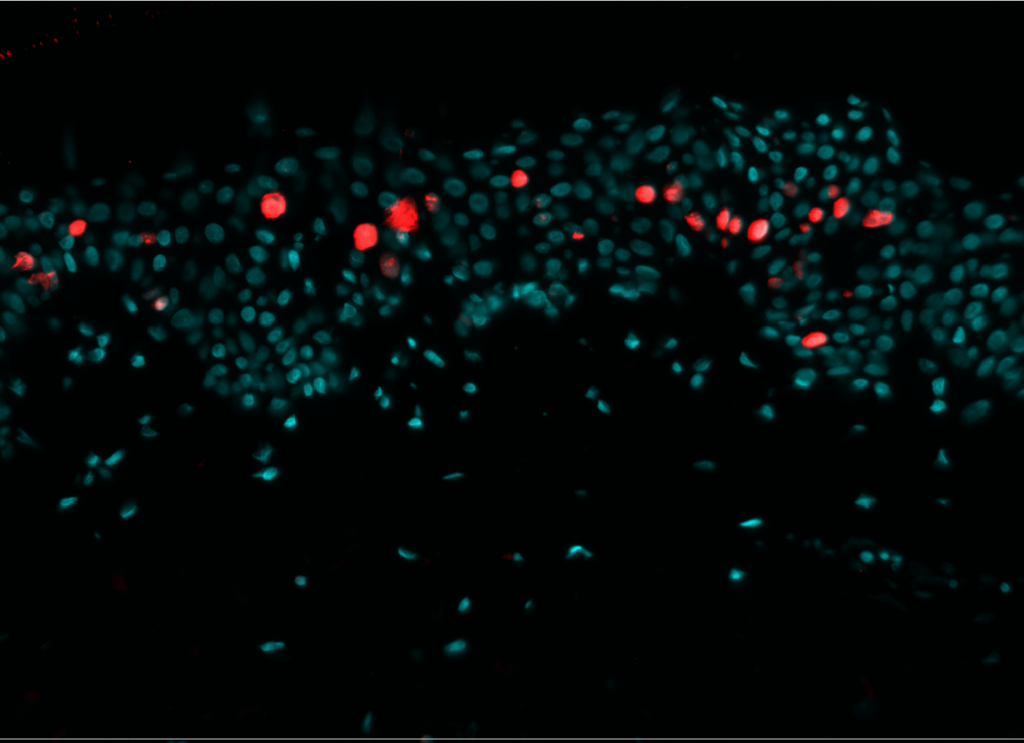

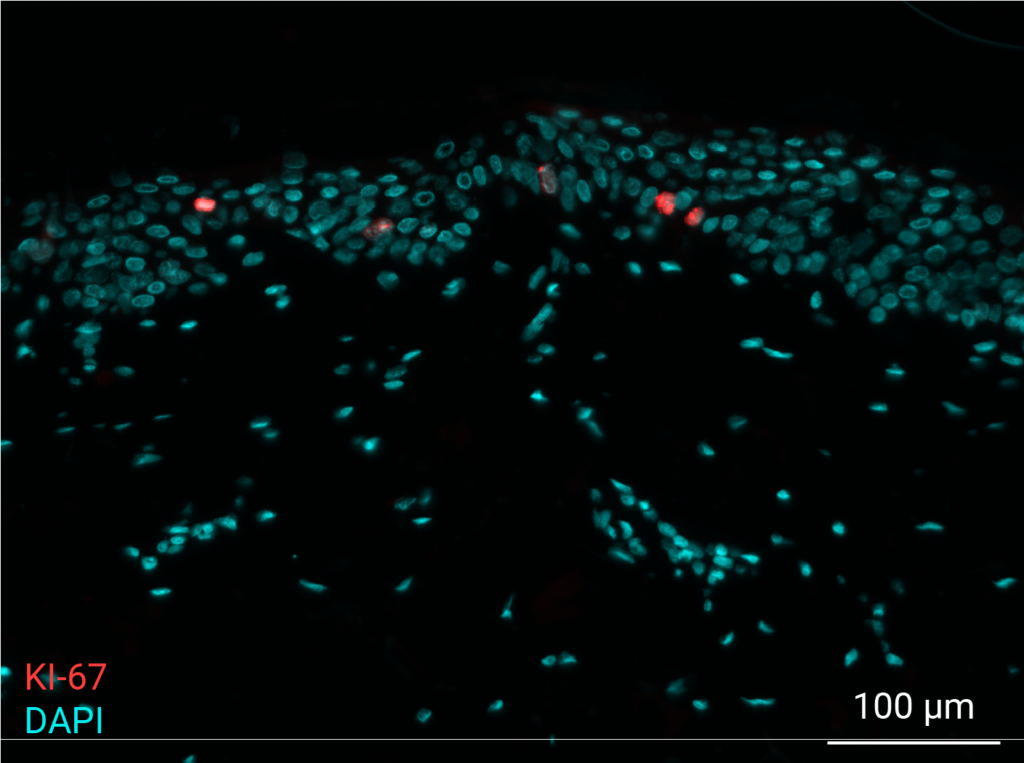

Pollution exposure decreases cell proliferation. Cell proliferation was analyzed by immunostaining of NativeSkin® model for Ki-67. Proliferative cells were normally present in the non-polluted NativeSkin® models from day 0 to day 4. Exposure to pollution induced a 3.7 fold decrease of Ki-67 positive cells in the epidermis as compared to control.
Exposure of NativeSkin® to UV-rays
NativeSkin® is a relevant tool to assess protection against UVB damage. In order to demonstrate the response to UVB-rays, we irradiated NativeSkin® models with UVB dosed at 250 mJ/cm2 and 500 mJ/cm2 and compared the results with non-irradiated models.
Oxidative stress
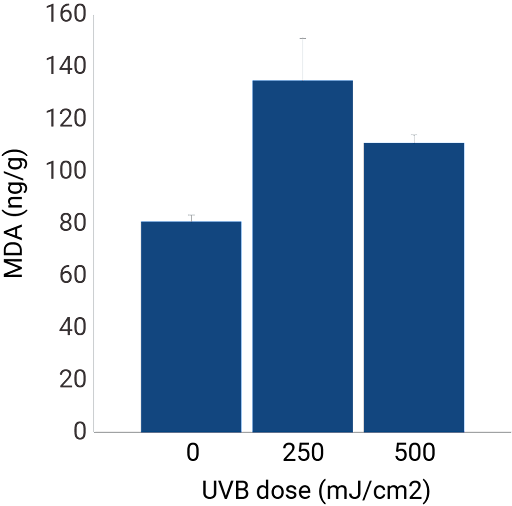

Malondialdehyde (MDA) measurement: as UVB radiation causes an increase in oxidative stress, we measured MDA formation in NativeSkin® samples. Results show an increase of MDA formation in the samples that were irradiated with UVB.
Cell apoptosis & thymine dimer formation


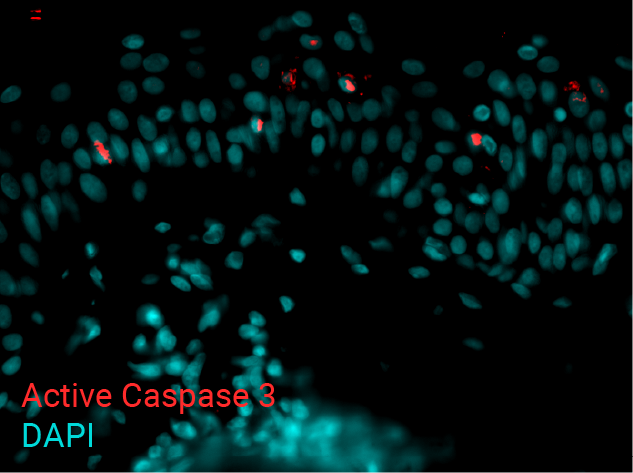

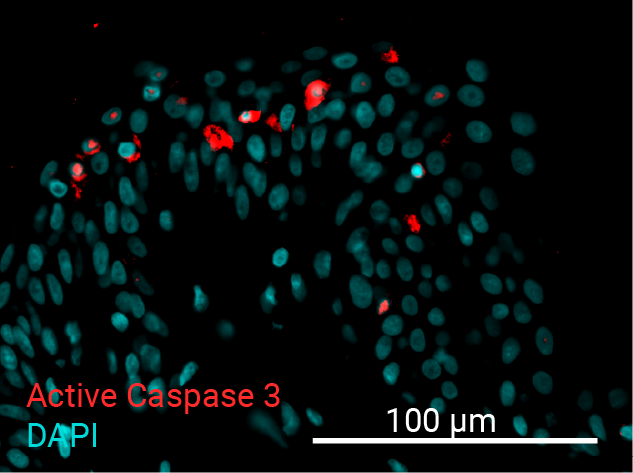

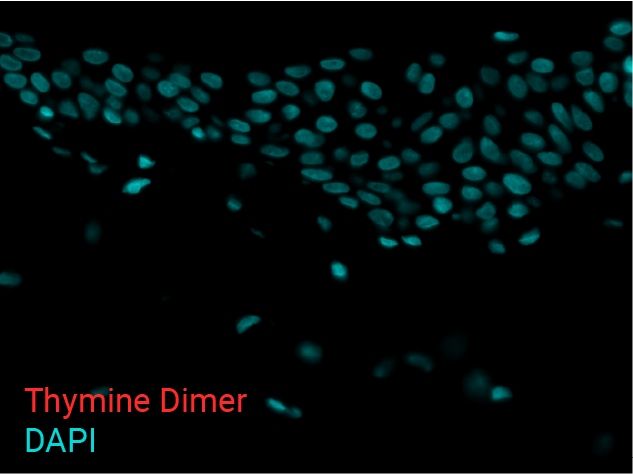

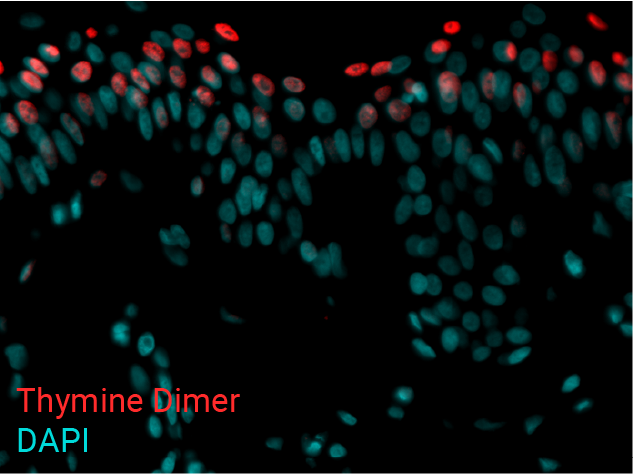

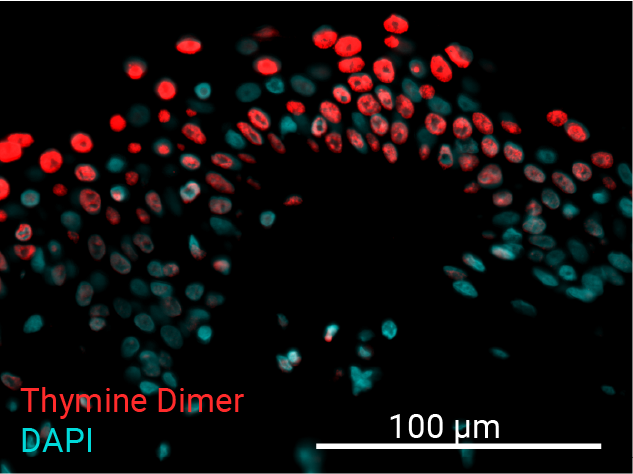

The results show that UVB induces important skin damage in NativeSkin® models. Immunostaining with anti-active Caspase 3 shows an important increase in cell apoptosis induced by UVB radiation. Immunostaining with anti-thymine dimer shows an important increase in the formation of thymine dimer, meaning that UVB radiation induces DNA damage in skin cells.
A versatile study platform for first-in-human data
Easy & relevant study results after topical and systemic administration
The NativeSkin® model is very versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications thanks to its unique configuration. The presence of human epidermis and dermis in the NativeSkin® model allows for systemic treatments and genomic readouts to study how skin cells and appendages respond to your compound after it has been added to the culture medium. The larger NativeSkin® models come with a silicone ring, which prevents compounds from leaking into the culture medium. This approach allows for true topical application in a sealed environment and relevant data for skin absorption and barrier function studies.


Systemic administration


Topical application
A wide range of applications
Pick the right method to assess your drug, cosmetic or medical device




The NativeSkin® model is suitable for a wide range of applications including preclinical efficacy and toxicity studies as well as cosmetic claim substantiation. The model is frequently used to evaluate all kinds of compounds, active ingredients and finished products, such as lotions, gels, creams… as well as medical devices, such as microneedle array patches (MAPs). Below, you’ll find some examples of the types of studies you can conduct with the NativeSkin® model.
Skin delivery
Topical absorption & effects on skin metabolism
Toxicity
Compound toxicity & effects on barrier function
Wound healing
Wound healing properties & microbial colonisation
Skin microbiome
Effects on the skin microbiome & microbial colonization
- Viability assay (MTT/WST-8)
- Formalin fixation for paraffin embedding
- OCT fixation and cryosectioning
- Epidermal separation (with Dispase and heat-mediated)
- H&E staining
- Fontana Masson staining
- Lucifer Yellow penetration
- Human keratinocyte primary culture
- RNA extraction
- Immunofluorescence staining
One model, two ways to get the results you need
Pick your preferred option & get your study going




NativeSkin® is available as an in-house service to conduct custom studies for a wide range of applications. Don’t hesitate to use our 10 years of experience so we can help you obtain relevant results to move your research forward. However, should you prefer to conduct the studies in your own labs, don’t hesitate to order directly via our online platform, as NativeSkin® is also the only human skin model available for shipment around the world.
Scientific publications using NativeSkin®
See how others use the NativeSkin® model to generate results




March 2024 - In vitro studies into establishing therapeutic bioequivalence of complex topical products: weight of evidence.
Published in Science Direct – March 25, 2024. 124012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124012.
Margarida Miranda, Zoe Volmer, Alicia Cornick, Aidan Goody, Catarina Cardoso, Alberto A.C.C. Pais, Marc Brown, Carla Vitorino
December 2023 - Redefine photoprotection: Sun protection beyond sunburn.
Published in Experimental dermatology Wiley – December 15, 2023. Exp Dermatol. 2024;33:e15002. doi:10.1111/exd.15002.
Mirja van Bodegraven, Marius Kröger, Daniela F. Zamudio Díaz, Silke B. Lohan, Rose K. C. Moritz, Nadine Möller, Chiara Knoblich, Alexandra Vogelsang, Zorica Milinic, Matthias Hallhuber, Julia M. Weise, Ludger Kolbe, Julia Gallinger, Cindy Graupner, Holger Klose, Claas Ulrich, Martina C. Meinke
November 2023 - N-acetyl-L-hydroxyproline: A potent skin anti-ageing active preventing advanced glycation end-product formation in vitro and ex vivo
Published in International of Cosmetics Science – November 27, 2023.
Chiara Knoblich, Katja Dunckelmann, Andrea Krüger, Thomas Küper, Thomas Blatt, Julia M Weise
September 2023 - Household laundry detergents disrupt barrier integrity and induce inflammation in mouse and human skin.
Published in European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 2023 – September 27, 2023.
Arturo O. Rinaldi, Manru Li, Elena Barletta, Paolo D’Avino, Duygu Yazici, Yagiz Pat, Siobhan Ward, Daniel Burla, Ge Tan, Nima Askary, Rasmus Larsson, Jeremy Bost, Huseyn Babayev, Raja Dhir, Nicolas Gaudenzio, Mubeccel Akdis, Kari Nadeau, Cezmi A. Akdis, Yasutaka Mitamura
August 2023 - M1/M2 Macrophage Skewing is Related to Reduction in Type I, V and VI Collagens with Aging in Sun-exposed Human Skin
Published in JID Innovations, 2023, 100222, ISSN 2667-0267 – August 11, 2023.
Satoshi Horiba, Munetaka Kawamoto, Ryozo Tobita, Ryota Kami, Yuki Ogura, Junichi Hosoi
August 2023 - Hydrogel degradation promotes angiogenic and regenerative potential of cell spheroids for wound healing
Published in Materials Today Bio – Volume 22, 2023,100769, ISSN 2590-0064; Published: 29 September 2022.
Victoria L. Thai, David H. Ramos-Rodriguez, Meron Mesfin, J. Kent Leach.
August 2023 - Copper-based dressing: Efficacy in a wound infection of ex vivo human skin
Published in Tissue&Cell (Volume 84, October 2023, 102196) – August 22, 2023.
Aaron D. Strickland, Mehmet Ozturk, Tricia Conti, Fahimeh Tabatabaei
April 2023 - Mast cell tolerance in the skin microenvironment to commensal bacteria is controlled by fibroblasts
Published in National Library of Medicine – April 28, 2023.
Anna Di Nardo, Yu-Ling Chang, Shahrzad Alimohammadi, Kana Masuda-Kuroki, Zhenping Wang, Krishna Sriram, Paul A Insel
March 2023 - Dissolvable microneedles for transdermal drug delivery showing skin penetration and modified drug release
Published in European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (Volume 182, 1 March 2023, 106371) – March 1, 2023.
Irina Iachina, André H Eriksson, Malene Bertelsen, Karsten Petersson, Jörgen Jansson, Pernille Kemp, Karen M Engell, Jonathan R Brewer, Kim T Nielsen
March 2023 - A Needle-free Transdermal Patch for Sampling Interstitial Fluid
Published in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering ( Volume: 70, Issue: 9, September 2023) – March 8, 2023.
D. J. O’Brien, D. Mills, J. Farina and M. Paranjape
January 2022 - Characterization of a novel non-steroidal glucocorticoid receptor agonist optimized for topical treatment
- Characterization of a novel non-steroidal glucocorticoid receptor agonist optimized for topical treatment
- Published in Nature – Scientific Reports – volume 12, Article number: 1501 (2022)
- Stefan Eirefelt, Martin Stahlhut, Naila Svitacheva, Martin A. Carnerup, Joel Mauricio Correa Da Rosa, David Adrian Ewald, Troels T. Marstrand, Mikkel Krogh-Madsen, Georg Dünstl, Kevin Neil Dack, Anna Ollerstam & Hanne Norsgaard
- Published in Nature – Scientific Reports – volume 12, Article number: 1501 (2022)
January 2022 - Polymethoxyflavones from Kaempferia parviflora ameliorate skin aging in primary human dermal fibroblasts and ex vivo human skin
- Polymethoxyflavones from Kaempferia parviflora ameliorate skin aging in primary human dermal fibroblasts and ex vivo human skin
- Published in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy – 2022 Jan;145:112461
- Wannita Klinngam, Phetploy Rungkamoltip, Saowarose Thongin, Jaruwan Joothamongkhon, Phattharachanok Khumkhrong, Mattaka Khongkow, Katawut Namdee, Surapun Tepaamorndech, Puxvadee Chaikul, Mayuree Kanlayavattanakul, Nattaya Lourith, Kitiya Piboonprai, Uracha Ruktanonchai, Udom Asawapirom, Tawin Iempridee
- Published in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy – 2022 Jan;145:112461
December 2021 - Barrier disruption, dehydration and inflammation: Investigation of the vicious circle underlying dry skin
- Barrier disruption, dehydration and inflammation: Investigation of the vicious circle underlying dry skin
-
- Published in International Journal of Cosmetic Science – 2021 Dec;43(6):729-737
- Cécile Bize, Erwan Le Gélébart, Alain Moga, Bruno Payré, Christine Garcia
- Published in International Journal of Cosmetic Science – 2021 Dec;43(6):729-737
December 2021 - A hypothetical skin sensitisation next generation risk assessment for coumarin in cosmetic products
- A hypothetical skin sensitisation next generation risk assessment for coumarin in cosmetic products
- Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology – 2021, 105075, ISSN 0273-2300
- G. Reynolds, J. Reynolds, N. Gilmour, R. Cubberley, S. Spriggs, A. Aptula, K. Przybylak, S. Windebank, G. Maxwell, M.T. Baltazar
- Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology – 2021, 105075, ISSN 0273-2300
October 2021 - The anti-wrinkles properties of sodium acetylated hyaluronate
- The anti-wrinkles properties of sodium acetylated hyaluronate
- Published in Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology – 28 October 2021
- Marie Meunier MS, Amandine Scandolera PhD, Emilie Chapuis BS, Laura Lapierre BS, Jérôme Sandré MD, Gerhard Brunner PhD, Martin Lovchik PhD, Romain Reynaud MS
- Published in Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology – 28 October 2021
October 2021 - A proof-of-concept study utilising 2D NMR spectrometry for in situ characterisation and quantitation of key biomarkers and actives in tape stripped ex vivo human skin
- A proof-of-concept study utilising 2D NMR spectrometry for in situ characterisation and quantitation of key biomarkers and actives in tape-stripped ex vivo human skin
- Published in Talanta – October 2021
- Cameron Robertson, Nidhin Raj b, Robert Lucas b, Tomris Coban a, Adam Le Gresley
- Published in Talanta – October 2021
September 2021 - Clinical brightening efficacy and safety of Melasolv™ (3,4,5-trimethoxy cinnamate thymol ester, TCTE) in Southeast Asian women
- Clinical brightening efficacy and safety of Melasolv™ (3,4,5-trimethoxy cinnamate thymol ester, TCTE) in Southeast Asian women
- Published in Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology – 2021 Sep;20(9):2851-2859
- Seung Hun Kim, Byung Ryol Paik, Sung Hoon Lee, So Mi Lee, Mi Jin Kim, Eun Joo Kim, Chin Yong Leow, Changhui Cho, Won-Seok Park, Byung-Fhy Suh
- Published in Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology – 2021 Sep;20(9):2851-2859
February 2021 - hiPSC-Derived Epidermal Keratinocytes from Ichthyosis Patients Show Altered Expression of Cornification Markers
- hiPSC-Derived Epidermal Keratinocytes from Ichthyosis Patients Show Altered Expression of Cornification Markers
- Published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences – 2021 Feb 11;22(4):1785
- Dulce Lima Cunha, Amanda Oram, Robert Gruber, Roswitha Plank, Arno Lingenhel, Manoj K Gupta, Janine Altmüller, Peter Nürnberg, Matthias Schmuth, Johannes Zschocke, Tomo Šarić, Katja M Eckl, Hans C Hennies
- Published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences – 2021 Feb 11;22(4):1785
January 2021 - Challenges in Developing a Human Model System for Skin Microbiome Research
- Challenges in Developing a Human Model System for Skin Microbiome Research
- Published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology – 2021 Jan;141(1):228-231.e4.
- Peter J Larson, Derrick Chong, Elizabeth Fleming, Julia Oh
- Published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology – 2021 Jan;141(1):228-231.e4.
December 2020 - Active neutrophil responses counteract Candida albicans burn wound infection of ex vivo human skin explants
- Active neutrophil responses counteract Candida albicans burn wound infection of ex vivo human skin explants
- Published in Scientific Reports – 2020 Dec 11;10(1):21818
- Christin von Müller, Fionnuala Bulman, Lysett Wagner, Daniel Rosenberger, Alessandra Marolda, Oliver Kurzai, Petra Eißmann, Ilse D Jacobsen, Birgit Perner, Peter Hemmerich, Slavena Vylkova
- Published in Scientific Reports – 2020 Dec 11;10(1):21818
November 2020 - Synthesis of Kisspeptin-Mimicking Fragments and Investigation of their Skin Anti-Aging Effects
- Synthesis of Kisspeptin-Mimicking Fragments and Investigation of their Skin Anti-Aging Effects
- Published in International Journal of Molecular Science – 2020 Nov; 21(22): 8439
- Kyung-Eun Lee, Sugyeong Jeong, Seok Kyun Yun, Seoyeon Kyung, Abadie Sophie, Sang Hyun Moh, Hyo Hyun Seo, Myeong Sam Park, Seunghyun Kang, and Hyeonju Yeo
- Published in International Journal of Molecular Science – 2020 Nov; 21(22): 8439
September 2020 - A novel skin brightening topical technology
- A novel skin brightening topical technology
- Published in Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology – 28 September 2020; 19: 3280– 3285
- Zoe Diana Draelos MD, Isabel Diaz BA, Aaron Cohen PhD, Junhong Mao PhD, Thomas Boyd PhD
- Published in Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology – 28 September 2020; 19: 3280– 3285
July 2020 - Highly accurate skin-specific methylome analysis algorithm as a platform to screen and validate therapeutics for healthy aging
- Highly accurate skin-specific methylome analysis algorithm as a platform to screen and validate therapeutics for healthy aging
- Published in Clinical Epigenetics – 12, Article number: 105 (2020)
- Mariana Boroni, Alessandra Zonari, Carolina Reis de Oliveira, Kallie Alkatib, Edgar Andres Ochoa Cruz, Lear E. Brace & Juliana Lott de Carvalho
- Published in Clinical Epigenetics – 12, Article number: 105 (2020)
April 2020 - Identification of Malassezia furfur Secreted Aspartyl Protease 1 (MfSAP1) and Its Role in Extracellular Matrix Degradation
- Identification of Malassezia furfur Secreted Aspartyl Protease 1 (MfSAP1) and Its Role in Extracellular Matrix Degradation
- Published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology – 2020 Apr 9; 10: 148
- Si En Poh, Joleen P. Z. Goh, Chen Fan, Wisely Chua, Shi Qi Gan, Priscilla Lay Keng Lim, Bhavya Sharma, David I. Leavesley, Thomas L. Dawson, Jr., and Hao Li
- Published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology – 2020 Apr 9; 10: 148
April 2020 - Single-cell transcriptomes of the human skin reveal age-related loss of fibroblast priming
- Single-cell transcriptomes of the human skin reveal age-related loss of fibroblast priming
- Published in Communications Biology volume 3, Article number: 188 (2020)
- Llorenç Solé-Boldo, Günter Raddatz, Sabrina Schütz, Jan-Philipp Mallm, Karsten Rippe, Anke S. Lonsdorf, Manuel Rodríguez-Paredes & Frank Lyko
- Published in Communications Biology volume 3, Article number: 188 (2020)
January 2020 - Mapping 2D- and 3D-distributions of metal/metal oxide nanoparticles within cleared human ex vivo skin tissues
- Mapping 2D- and 3D-distributions of metal/metal oxide nanoparticles within cleared human ex vivo skin tissues
- Published in NanoImpact – 2020 Jan;17:100208
- George J Touloumes, Herdeline Ann M Ardoña, Evan K Casalino, John F Zimmerman, Christophe O Chantre, Dimitrios Bitounis, Philip Demokritou, Kevin Kit Parker
- Published in NanoImpact – 2020 Jan;17:100208
January 2020 - Epidermal and Dermal Hallmarks of Photoaging are Prevented by Treatment with Night Serum Containing Melatonin, Bakuchiol, and Ascorbyl Tetraisopalmitate: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies
- Epidermal and Dermal Hallmarks of Photoaging are Prevented by Treatment with Night Serum Containing Melatonin, Bakuchiol, and Ascorbyl Tetraisopalmitate: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies
- Published in Dermatology & Therapy (Heidelberg) – 2020 Feb;10(1):191-202.
- Mridvika Narda, Anthony Brown, Béatrice Muscatelli-Groux, Jean A Grimaud, Corinne Granger
- Published in Dermatology & Therapy (Heidelberg) – 2020 Feb;10(1):191-202.
January 2020 - Anti-Wrinkle Benefits of Peptides Complex Stimulating Skin Basement Membrane Proteins Expression
- Anti-Wrinkle Benefits of Peptides Complex Stimulating Skin Basement Membrane Proteins Expression
- Published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences – 2020 Jan; 21(1): 73
- Sekyoo Jeong, Seokjeong Yoon, Sungwoo Kim, Juyeon Jung, Myungho Kor, Kayoung Shin, Chaejin Lim, Hyo Sun Han, Haekwang Lee, Kyeong-Yong Park, Jinwan Kim, Hwa Jee Chung, and Hyun Jung Kim
- Published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences – 2020 Jan; 21(1): 73
2019 - An Efficient Means to Mitigate Skin Inflammaging by Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Nfkb Pathways: A Novel Epigenetic Mechanism
- An Efficient Means to Mitigate Skin Inflammaging by Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Nfkb Pathways: A Novel Epigenetic Mechanism
- Published in IFSCC Magazine 3 – 2019
- Hanane Chajra, Sandrine Delaunois, David Garandeau, Gaelle Saint-Auret, Marisa Meloni, Eunsun Jung, Mathilde Frechet
- Published in IFSCC Magazine 3 – 2019
September 2019 - Peptidylarginine Deiminase Inhibitor Cl-Amidine Attenuates Cornification and Interferes with the Regulation of Autophagy in Reconstructed Human Epidermis
- Peptidylarginine Deiminase Inhibitor Cl-Amidine Attenuates Cornification and Interferes with the Regulation of Autophagy in Reconstructed Human Epidermis
- Published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology – 2019 Sep;139(9):1889-1897.e4.
- Laura Cau, Hidenari Takahara, Paul R Thompson, Guy Serre, Marie-Claire Méchin, Michel Simon
- Published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology – 2019 Sep;139(9):1889-1897.e4.
September 2019 - A human skin model to evaluate the protective effect of compounds against UVA damage
- A human skin model to evaluate the protective effect of compounds against UVA damage
- Published in International Journal of Cosmetic Science – 12 September 2019
- S. Abadie, P. Bedos, J. Rouquette
- Published in International Journal of Cosmetic Science – 12 September 2019
September 2019 - Poster - Scientific Visualisation of Skin Damage caused by Irritants in Human Skin
- Scientific Visualisation of Skin Damage caused by Irritants in Human Skin
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
- Nidhin Raj, Robert Lucas, Sarah Coomasaru, Behfar Moghaddam, Ian Francis, Paul McGill – GlaxoSmithKline Consumer Healthcare, Weybridge, United Kingdom
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
September 2019 - Poster - Ex vivo visualization and extended release from a dissolvable microarray
- Ex vivo visualization and extended release from a dissolvable microarray
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
- K. T. Nielsen, A. H. Eriksson, M. F. Carlsen, K. M. Engel, J. Jansson, K. Petersson, M. A. Røpke, M. Bertelsen, P. Kemp –
LEO Pharma A/S, Ballerup, Denmark
- K. T. Nielsen, A. H. Eriksson, M. F. Carlsen, K. M. Engel, J. Jansson, K. Petersson, M. A. Røpke, M. Bertelsen, P. Kemp –
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
September 2019 - Poster - Preservation of human skin integrity and metabolism during 10 days in culture with NativeSkin® system
- Preservation of human skin integrity and metabolism during 10 days in culture with NativeSkin® system
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
- E. Raude (Genoskin), E. Pagès (Genoskin), M. Pastore (Genoskin), P.-O. Cuoc (Promega), L. Malaquin (LAAS-CNRS), P. Descargues (Genoskin)
- Scientific Poster presented at the 2019 Congress of the European Society for Dermatological Research (ESDR) – September 18-21, 2019
July 2019 - The Actin-Based Motor Myosin Vb Is Crucial to Maintain Epidermal Barrier Integrity
- The Actin-Based Motor Myosin Vb Is Crucial to Maintain Epidermal Barrier Integrity
- Published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology – July 1, 2019, Volume 139, Issue 7, P1430-1438
- Marie Reynier, Sophie Allart, Dominique Goudounèche, Alain Moga, Guy Serre, Michel Simon, Corinne Leprince
- Published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology – July 1, 2019, Volume 139, Issue 7, P1430-1438
June 2019 - The Amino-Terminal Part of Human FLG2 Is a Component of Cornified Envelopes
- The Amino-Terminal Part of Human FLG2 Is a Component of Cornified Envelopes
- Published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology – 2019 Jun;139(6):1395-1397.
- Géraldine Albérola, Jens-Michael Schröder, Carine Froment, Michel Simon
- Published in Journal of Investigative Dermatology – 2019 Jun;139(6):1395-1397.
December 2018 - Melatonin, bakuchiol and ascorbyl tetraisopalmitate synergize to modulate gene expression and restore Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 signaling in UV-exposed skin
- Melatonin, bakuchiol and ascorbyl tetraisopalmitate synergize to modulate gene expression and restore Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 signaling in UV-exposed skin
- Published in Cellular and Molecular Biology – 2018 Dec 31;65(8):39-47.
- Mridvika Narda, Anthony Brown, Daniel Pérez-Cremades, José Luís García-Giménez, Corinne Granger
- Published in Cellular and Molecular Biology – 2018 Dec 31;65(8):39-47.
October 2018 - Phenotypic and lipidomic characterization of primary human epidermal keratinocytes exposed to simulated solar UV radiation
- Phenotypic and lipidomic characterization of primary human epidermal keratinocytes exposed to simulated solar UV radiation
- Published in Journal of Dermatological Science – 2018 Oct;92(1):97-105.
- Núria Dalmau, Nathalie Andrieu-Abadie, Romà Tauler, Carmen Bedia
- Published in Journal of Dermatological Science – 2018 Oct;92(1):97-105.
October 2018 - Myosin phosphatase accelerates cutaneous wound healing by regulating migration and differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes via Akt signaling pathway in human and murine skin
- Myosin phosphatase accelerates cutaneous wound healing by regulating migration and differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes via Akt signaling pathway in human and murine skin
- Published in Molecular Basis of Disease – Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – 2018 Oct;1864(10):3268-3280.
- Dániel Horváth, Adrienn Sipos, Evelin Major, Zoltán Kónya, Róbert Bátori, Dóra Dedinszki, Attila Szöll Si, István Tamás, Judit Iván, Andrea Kiss, Ferenc Erd di, Beáta Lontay
- Published in Molecular Basis of Disease – Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – 2018 Oct;1864(10):3268-3280.
May 2018 - 3D imaging of cleared human skin biopsies using light-sheet microscopy: A new way to visualize in-depth skin structure
- 3D imaging of cleared human skin biopsies using light-sheet microscopy: A new way to visualize in-depth skin structure
- Published in Skin Research & Technology – 2018 May;24(2):294-303.
- S Abadie, C Jardet, J Colombelli, B Chaput, A David, J-L Grolleau, P Bedos, V Lobjois, P Descargues, J Rouquette
- Published in Skin Research & Technology – 2018 May;24(2):294-303.
May 2018 - Poster - 3D imaging of cleared ex vivo normal human skin, skin appendages and psoriasiform skin lesion using light-sheet microscopy
- 3D imaging of cleared ex vivo normal human skin, skin appendages and psoriasiform skin lesion using light-sheet microscopy
- Scientific Poster presented at the International Investigative Dermatology (IID) 2018 Meeting – 16-19 May 2018
- C. Jardet (Genoskin), S. Abadie (Syntivia), M. Pastore (Genoskin), J. Colombelli (Advanced Digital Microscopy – IRB), B. Chaput (CHU Toulouse Rangueil), A. David (Genoskin), J.-L. Grolleau (CHU Toulouse Rangueil), P. Bedos (Syntivia), V. Lobjois (ITAV), P. Descargues (Genoskin), J. Roquette (ITAV)
- Scientific Poster presented at the International Investigative Dermatology (IID) 2018 Meeting – 16-19 May 2018
May 2018 - Poster - NativeSkin®, an immunocompetent human skin model to study antigen uptake and processing by Langerhans cells
- NativeSkin®, an immunocompetent human skin model to study antigen uptake and processing by Langerhans cells
- Scientific Poster presented at the International Investigative Dermatology (IID) 2018 Meeting – 16-19 May 2018
- E. Pagès (Genoskin), L. Mondoulet (DBV Technologies), E. Bonnefont (Genoskin), E. Braun (Genoskin), V. Dhelft (DBV Technologies), C. Dupont (Hôpital Necker, Université Paris-Descartes), H. Sampson (DBV Technologies), P. Descargues (Genoskin)
- Scientific Poster presented at the International Investigative Dermatology (IID) 2018 Meeting – 16-19 May 2018
September 2017 - Oxidative damage and impairment of protein quality control systems in keratinocytes exposed to a volatile organic compounds cocktail
- Oxidative damage and impairment of protein quality control systems in keratinocytes exposed to a volatile organic compounds cocktail
- Published in Scientific Reports – 06 September 2017
- Marlène Dezest, Mickael Le Bechec, Laurent Chavatte, Valérie Desauziers, Benoît Chaput, Jean-Louis Grolleau, Pascal Descargues, Carine Nizard, Sylvianne Schnebert, Sylvie Lacombe & Anne-Laure Bulteau
- Published in Scientific Reports – 06 September 2017
June 2017 - SIRT1 activation mediates heat-induced survival of UVB damaged Keratinocytes
- SIRT1 activation mediates heat-induced survival of UVB damaged Keratinocytes
- Published in BMC Dermatology – 10 June 2017
- Leslie Calapre, Elin S. Gray, Sandrine Kurdykowski, Anthony David, Pascal Descargues & Mel Ziman
- Published in BMC Dermatology – 10 June 2017
January 2017 - Mechanistic insights into the impact of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on human epithelial cell lines
- Mechanistic insights into the impact of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on human epithelial cell lines
- Published in Scientific Reports – 25 January 2017
- Marlène Dezest, Laurent Chavatte, Marion Bourdens, Damien Quinton, Mylène Camus, Luc Garrigues, Pascal Descargues, Stéphane Arbault, Odile Burlet-Schiltz, Louis Casteilla, Franck Clément, Valérie Planat & Anne-Laure Bulteau
- Published in Scientific Reports – 25 January 2017
2016 - In vitro Dermal Absorption of Hydroquinone: Protocol Validation and Applicability on Illegal Skin-Whitening Cosmetics
- In vitro Dermal Absorption of Hydroquinone: Protocol Validation and Applicability on Illegal Skin-Whitening Cosmetics
- Published in Skin Pharmacology & Physiology – 2016;29(6):300-308.
- Bart Desmedt, Gamze Ates, Patricia Courselle, Jacques O De Beer, Vera Rogiers, Benoit Hendrickx, Eric Deconinck, Kristien De Paepe
- Published in Skin Pharmacology & Physiology – 2016;29(6):300-308.
November 2016 - Integrating targeted gene expression and a skin model system to identify functional inhibitors of the UV activated p38 MAP kinase
- Integrating targeted gene expression and a skin model system to identify functional inhibitors of the UV activated p38 MAP kinase
- Published in Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences – 2016 Nov 30;15(12):1468-1475.
- Amaal Abrahams, Nicolas Mouchet, Nicolas Gouault, Françoise Lohézic Le Dévéhat, Myriam Le Roch, Isabelle Rouaud, David Gilot, Marie-Dominique Galibert
- Published in Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences – 2016 Nov 30;15(12):1468-1475.
May 2016 - Heat-mediated reduction of apoptosis in UVB-damaged keratinocytes in vitro and in human skin ex vivo
- Heat-mediated reduction of apoptosis in UVB-damaged keratinocytes in vitro and in human skin ex vivo
- Published in BMC Dermatology – 2016 May 26;16(1):6.
- Leslie Calapre, Elin S Gray, Sandrine Kurdykowski, Anthony David, Prue Hart, Pascal Descargues, Mel Ziman
- Published in BMC Dermatology – 2016 May 26;16(1):6.
October 2015 - In vitro and in vivo dermal absorption assessment of acetyl aspartic acid: a compartmental study
- In vitro and in vivo dermal absorption assessment of acetyl aspartic acid: a compartmental study
- Published in International Journal of Cosmetic Science – 2015 Oct;37 Suppl 1:34-40.
- L Duracher, L Visdal-Johnsen, A Mavon
- Published in International Journal of Cosmetic Science – 2015 Oct;37 Suppl 1:34-40.
October 2015 - Safety assessment of a novel active ingredient, acetyl aspartic acid, according to the EU Cosmetics Regulation and the Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety guidelines
- Safety assessment of a novel active ingredient, acetyl aspartic acid, according to the EU Cosmetics Regulation and the Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety guidelines
- Published in International Journal of Cosmetic Science – 2015 Oct;37 Suppl 1:21-7.
- P Daly, G Moran
- Published in International Journal of Cosmetic Science – 2015 Oct;37 Suppl 1:21-7.
March 2015 - A Novel Explant Model for Skin Delivery Assessment
- A Novel Explant Model for Skin Delivery Assessment
- Published in Cosmetics & Toiletries – March 1, 2015
- Lucie Duracher, PhD; Lene Visdal-Johnsen, PhD; and Alain Mavon, PhD; Sandrine Kurdykowski, PhD; and Pascal Descargues, PhD
- Published in Cosmetics & Toiletries – March 1, 2015
March 2015 - Human Skin Models for Research Applications in Pharmacology and Toxicology: Introducing NativeSkin®, the “Missing Link” Bridging Cell Culture and/or Reconstructed Skin Models and Human Clinical Testing
- Human Skin Models for Research Applications in Pharmacology and Toxicology: Introducing NativeSkin®, the “Missing Link” Bridging Cell Culture and/or Reconstructed Skin Models and Human Clinical Testing
- Published in Applied In Vitro Toxicology – 6 March 2015 Vol. 1, No.1
- Bart De Wever, Sandrine Kurdykowski, and Pascal Descargues
- Published in Applied In Vitro Toxicology – 6 March 2015 Vol. 1, No.1
October 2014 - Calcipotriol counteracts betamethasone-induced decrease in extracellular matrix components related to skin atrophy
- Calcipotriol counteracts betamethasone-induced decrease in extracellular matrix components related to skin atrophy
- Published in Archives of Dermatological Research – 2014 Oct;306(8):719-29.
- Hanne Norsgaard, Sandrine Kurdykowski, Pascal Descargues, Tatiana Gonzalez, Troels Marstrand, Georg Dünstl, Mads Røpke
- Published in Archives of Dermatological Research – 2014 Oct;306(8):719-29.